Describe the General Structure of Fibrous Joints
Up to 24 cash back The fibrous capsule for most joints is a firm structure consisting of dense connective tissue that invests the entire joint and usually inserts into the bones close to the articulating surfaces. Describe the general structure of fibrous joints.

Joint Fibrous Joints Britannica
Fibrous joints can be further sub-classified into sutures gomphoses and syndesmoses.

. These fixed or immovable joints are typically interlocked with irregular edges. Synovial joints are by far the most common classification of a joint within the human body. They are highly moveable and all have a synovial capsule collagenous structure surrounding the entire joint a synovial membrane the inner layer of the capsule which secretes synovial fluid a lubricating liquid and cartilage known as hyaline.
4 Describe how bones of cartilaginous joints are held together. The basic structure of a synovial joint the common accessory structures and their functions. Fibrous Joints The bones of fibrous joints are seized together by fibrous connective tissue.
Describe the general structure of cartilaginous joints. Based on the dominant type of periarticular connective tissue that reinforces the articulation synarthrodial joints can be further classified as fibrous or cartilaginous. Classify joints by structure and by function.
Fibrous joints consist of two bones that are united by fibroustissue and that exhibit little or no movement. Fibrous joints are connected by dense tough connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers. These are typically joints that require strength and stability over range of movement.
As the name indicates at a cartilaginous joint the adjacent bones are united by cartilage a tough but flexible type of connective tissue. No worries though since we will only focus on the few which are more common in terms of function and. Fibrous joints are where adjacent bones are strongly united by fibrous connective tissue.
1 bones joined by dense fibrous connective tissue. Name and give an example of each of the three common types of fibrous joints. Answer 2T View the full answer.
There are three types of fibrous joints. Answer On the basis of structure three types of joints are present. Many of the joints are moveable that allows the movement of the bones.
Fibrous cartilaginous and synovial. The synovial cavity also called joint cavity is the space between two articulating bones. Common types of fibrous joints.
Fibrous layer outer consists of white fibrous tissue known the capsular ligament. This is a tissue that covers the surface of a bone where there is joint. The articular cartilage covers and protects the bone ends.
A fibrous joint is one in which the two articulating bones are interconnected by dense or fibrous connective tissue. These joints have no cavity or space. Fibrous joints are stabilized by specialized dense connective tissues usually with a high concentration of collagen.
Fibrous Joints Fibrous Joints. Describe the general structure of fibrous joints. This chapter is intended to provide an overview of the basic structure and function of joints as a foundation for understanding the motion of individual body segments and the body as a whole.
1 List the functions of joints. The gap filled by connective tissue may be narrow or wide. Fibrous joints are also called fixed or immovable joints because they do not move.
The articular cartilage also acts as a shock absorber. Define joint or articulation. Name and give an example of each of the three common types of fibrous joints.
Joints can move a little amphiarthrosis a lot diarthrosis or not at all synarthrosis. The basic structure of a synovial joint consists of a synovial cavity articular cartilage a fibrous articular capsule and ligaments. The three types of fibrous joints are sutures gomphoses and syndesmoses.
Name and give an example of each of the two common types of cartilaginous joints. The articular capsule surrounds the joint and is continuous with the periosteum of articulating bones. A fibrous joint is where the bones are bound by a tough fibrous tissue.
There are three structural classifications of joints. The major categories of joints and the structure and function of each category. Fibrous cartilaginous and synovial joints.
2 Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together. Name and give an example of each of the three. 3 Describe how bones of fibrous joints are held together.
Examples of fibrous joints include the sutures of the skull the distal tibiofibular joint. It holds together the articulating bones and supports the underlying synovium. There are approximately 400 joints in the human body.
A joint is the. The thickness of the fibrous connective tissue connecting the two. Joints in this group are further subdivided on the basis of structure as sutures syn-desmoses or gomphoses.
Joints Classification of Joints 1. These types of joints lack a joint cavity and involve bones that are joined together by either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage There are two types of cartilaginous joints. Joints Learning Outcomes Define joint or articulation.
Answer - 1Joints means areas where 2 or more bones meet. 5 Describe the general structure of a synovial joint. Classify joints structurally and functionally.
Describe the general structure of fibrous joints. Describe the general structure of. It consists of two layers.
Sutures are immovable joints synarthrosis and are only found between the flat plate-like bones of the skull. A suture is the narrow synarthrotic joint that unites most bones of the skull. Objectives Define joint or articulation Classify joints on the basis of structure and function Describe the general structures of the different types of joints and give an example of each.
Joints also consist of the Cartilage. A suture is a type of fibrous joint synarthrosis bound by Sharpeys fibers that only occurs in the skull. The specific anatomic features of a joint play a large role in determining its range of motion degrees of freedom and overall functional potential.
Mo View the full answer. Sutures soochoorz are fibrous. The distance and direction a joint can move is called range of motion.

A General Synovial Joint Download Scientific Diagram
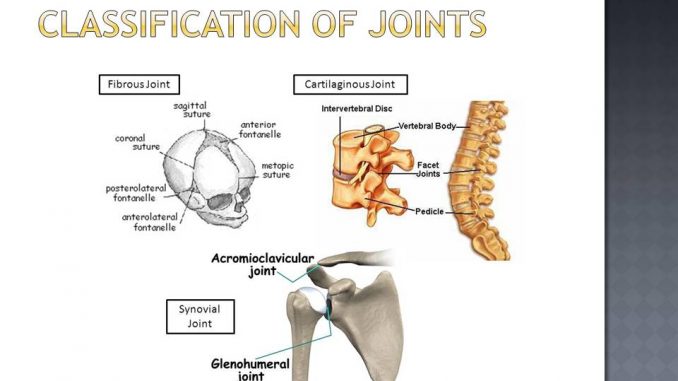
Classification Of Joints Online Biology Notes

Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology I

Joint Fibrous Joints Britannica

Tibia Fibula Human Skeleton Anatomy Human Body Anatomy Anatomy Bones

9 2 Fibrous Joints Anatomy Physiology

Instant Anatomy Upper Limb Joints Classification In 2021 Anatomy Education Medical School Stuff Human Anatomy And Physiology

Taproot And Fibrous Root Example Comparison Vector Illustration Scheme Vectormine Taproot Roots Drawing Root

Fibrous Joint Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Cross Section Diagram Of The Hair And Scalp Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Skin Facts

Difference Between Loose And Dense Connective Tissue Definition Characteristics Function Tissue Biology Loose Connective Tissue Nursing School Survival

Longitudinal View Neuron With Node Of Ranvier Neurons Nervous Nervous System

Fibrous Joints Structure Function Types Study Com

Types Classification Of Body Joints Cartilaginous Synovial Joint Hip Joint Anatomy Joints Anatomy Body Joints

College Of Arts And Sciences 404 Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology College Art

Cartilage Histology Elastic Cartilage Histology Slide Histology Slides Basic Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology

Good Poster Showing 11 Human Organ Systems Human Body Structure Human Body Systems Human Body Systems Activities


Comments
Post a Comment